Looking to increase your VO2 max and endurance? This article covers effective strategies on how to improve VO2 max quickly through training methods and nutrition tips.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding and measuring VO2 max is essential for tailoring training programs to improve cardiorespiratory fitness, cardiovascular fitness, and endurance.
- Effective training methods to improve VO2 max include High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT), Zone 2 endurance training, and Threshold training.
- Incorporating proper nutrition, recovery techniques, and supplementary exercises like strength training and circuit training can further amplify VO2 max improvements.
Understanding VO2 Max
VO2 max measures the maximum volume of oxygen your body can use during intense exercise, which is a key indicator of how efficiently your heart, lungs, and muscles work together.
Simply put, it is your body’s “horsepower” for physical activity—think of a high VO2 max as having a big engine in a car. This means that the higher your VO2 max, the easier and more effective your workouts will feel.
For context, the average VO2 max for untrained men is about 35 mL/kg/min, while for untrained women, it’s around 27 mL/kg/min. Elite endurance athletes, on the other hand, can reach values as high as 70 mL/kg/min. These numbers aren’t set in stone as VO2 max naturally declines by about 1% per year after age 30. Genetics also play a major role, accounting for up to 50% of the variability in VO2 max between individuals. But most people can still make significant improvements with proper training.
To highlight its importance, Peter Attia, MD, in his book notes:
“Keep in mind, increasing your VO2 max by any amount is going to improve your life, not only in terms of how long you live but also how well you live, today and in the future. Improving your VO2 max from the very bottom quartile to the quartile above (i.e., below average) is associated with almost a 50 percent reduction in all-cause mortality.” A higher VO2 max is strongly associated with a longer life.
Knowing your VO2 max can help you design workouts that match your current fitness level and track progress over time. Establishing a baseline measurement is important to monitor improvements. While elite athletes often monitor this number closely, everyday exercisers can also benefit.
You don’t need lab-grade equipment to reap the benefits. VO2 max is typically measured by analyzing oxygen consumption during exercise, often with specialized equipment, but there are also field tests and estimation methods. Simply being aware of what influences VO2 max, such as age, gender, and genetics, can help you make smarter training decisions. Regardless of your current fitness level, understanding your VO2 max is an effective way to personalize your fitness journey.
Primary Training Methods
How you train is key to improving your VO2 max. All effective training methods to improve VO2 max are built on regular aerobic activity. The most effective approaches focus on three primary components: High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT), Zone 2 Endurance Training, and Threshold and Tempo Training.
Each targets different parts of your aerobic system, working together to boost your cardiovascular fitness comprehensively.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)

HIIT is a form of high intensity workouts designed to maximize VO2 max improvements. It alternates bursts of intense effort with recovery periods, making it one of the fastest ways to raise your VO2 max. The well-known 4×4 protocol, that is, four minutes of hard exercise followed by four minutes of rest, repeated 4-6 times, is a classic example. This method pushes your heart rate to 90-95% of its max during work intervals, then allows recovery near 70%.
The power of HIIT lies in how it challenges your heart and muscles to use oxygen more efficiently. When you push your heart rate high, your body adapts by improving blood flow, increasing mitochondrial density, and impacting oxygen uptake, all critical for raising VO2 max.
To get the most from HIIT while avoiding burnout, follow these practical tips:
- Limit sessions to 1-3 times per week to ensure proper recovery.
- Work intervals should last 3-10 minutes at about 80-92% of your VO2 max pace for an optimal training effect.
- Recovery periods should allow your heart rate to drop to 60-70% of max before the next effort.
It really doesn’t matter whether you’re running, cycling, or using a rowing machine, HIIT can be adjusted to your fitness level and goals. Beyond boosting VO2 max, it also improves metabolism and endurance.
Zone 2 Endurance Training

Zone 2 training means exercising at a moderate pace, about 60-70% of your maximum heart rate, where fat is the primary fuel, and lactate levels stay low. This steady effort builds a strong aerobic foundation essential for more intense workouts.
But Zone 2 offers more than just physical benefits. Research shows that consistent Zone 2 training improves mental clarity and reduces daily fatigue by optimizing mitochondrial function, the tiny powerhouses in your cells responsible for energy production. This means you not only get fitter but also feel sharper and more energized throughout the day.
Typical Zone 2 activities include running, cycling, swimming, or hiking at a pace where you can comfortably hold a conversation. Sessions usually last 45-90 minutes, enough to stimulate mitochondrial growth without causing excessive fatigue.
Threshold and Tempo Training
Threshold training focuses on your lactate threshold (the point where lactic acid builds faster than your body can clear it), usually around 85% of your VO2 max pace. Training here teaches your body to sustain harder efforts longer.
A common approach is a 20-30 minute tempo run at this pace, roughly equivalent to a 15K race effort. Alternatively, tempo intervals like 3×10 minutes at threshold pace with short recovery jogs help you accumulate time at this intensity. Another method, over-under intervals, alternate just above and below your lactate threshold without full recovery, pushing your body’s ability to manage fatigue.
This type of training bridges the gap between easy aerobic work and all-out efforts, improving your capacity to maintain faster speeds for longer, which is an important factor in endurance performance.
Supplementary Training Methods
While primary training methods form the core of VO2 max improvement, supplementary training methods provide additional benefits that add to overall aerobic performance. These methods, including circuit training and strength training, complement the primary components and contribute to a well-rounded fitness routine. Supplementary training also supports the circulatory system by enhancing its ability to deliver oxygenated blood efficiently to working muscles, which is crucial for maximizing cardiovascular adaptations and athletic performance.
Additionally, supplementary methods are essential for improving VO2 max as they provide variety, prevent monotony, and spur new physiological adaptations. Incorporating these methods into your training routine achieves comprehensive cardiovascular and muscular benefits, strengthening overall fitness and performance.
Circuit Training

Circuit training combines aerobic and strength exercises in succession with minimal rest, offering comprehensive benefits for both VO2 max and muscular strength simultaneously.Body-weight circuits are highly effective and typically include exercises such as:
- Push-ups,
- Squats,
- Lunges,
- Burpees in a workout.
These exercises are performed for 30-60 seconds each, with 15-30 seconds transition time between stations.
This method increases your heart rate throughout the entire session, creating sustained cardiovascular demand that amplifies VO2 max while building muscular endurance. Resistance circuit training can produce 6.3% improvements in VO2 max while also developing strength, making it an efficient training method for time-constrained individuals.
Incorporating circuit training 2-3 times per week as supplementary training to primary endurance and interval sessions can diversify your workouts, preventing monotony and spurring new physiological adaptations that may lead to VO2 max improvements.
Strength Training

Strength training can moderately improve VO2 max by 6.3% when added to training programs, particularly through resistance circuit training protocols. Strength exercises improve muscular efficiency and oxygen utilization capacity, making muscles more effective at extracting and using oxygen during aerobic exercise.
Focus on compound movements like squats, lunges, deadlifts, and push-ups that engage multiple muscle groups and create cardiovascular demand. Strength training should complement, not replace,primary aerobic training methods and be performed 2-3 times per week on non-consecutive days.
Cross-training with different exercise modalities like swimming, cycling, or rowing challenges your body in new ways, prevents plateaus, and reduces the risk of overuse injuries. Integrating strength training into your fitness regime boosts muscular strength and supports aerobic capacity, contributing to VO2 max improvements.
Nutritional Strategies to Enhance VO2 Max
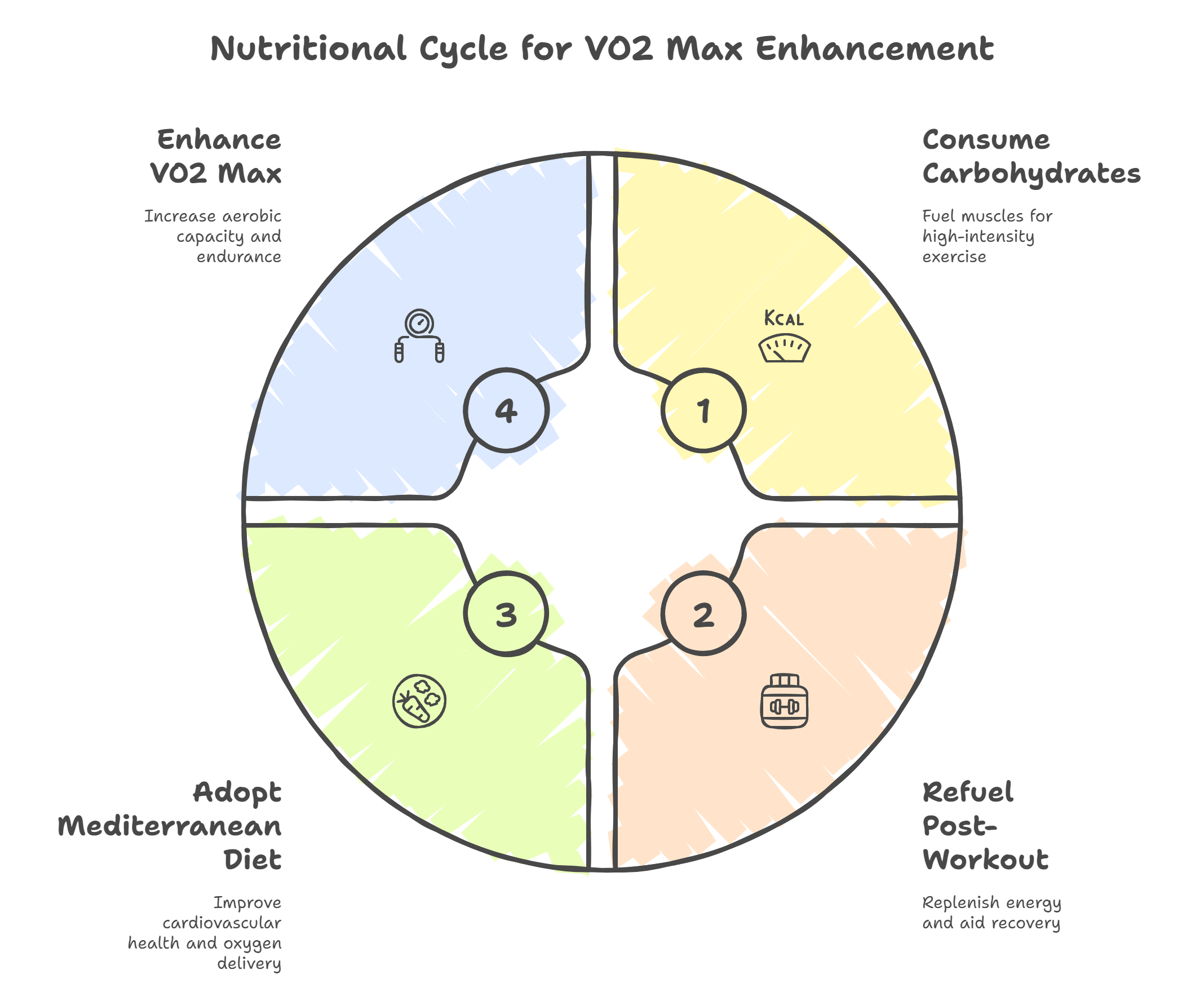
Proper nutrition is essential to support your training and maximize improvements in VO2 max. Among the key factors, carbohydrate intake plays a vital role in fueling endurance performance and increasing aerobic capacity. Proper nutrition also helps your body use more oxygen during intense exercise, supporting VO2 max improvements.
Additionally, adopting Mediterranean or plant-based diets has been linked to better cardiovascular health and higher VO2 max levels.
Carbohydrate Intake
Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for high-intensity exercise, providing the fuel your muscles need to sustain hard efforts and improve aerobic capacity. Consuming adequate carbs before and after workouts helps maintain energy levels and speeds recovery.
For example:
- Eat about 50 grams of carbohydrates roughly 2 hours before a HIIT session. A bowl of oatmeal topped with fresh fruit is a great choice.
- After training, refuel with a 30-gram protein-carb shake, such as whey protein blended with a banana, to aid muscle recovery and replenish glycogen stores.
Sample Carb-Rich Meals for VO2 Max Training
- Breakfast: Whole-grain toast with almond butter and sliced banana.
- Pre-workout snack: Greek yogurt with honey and berries.
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with chickpeas, mixed greens, and roasted vegetables.
- Post-workout: Smoothie with whey protein, spinach, frozen berries, and oats.
- Dinner: Brown rice with grilled salmon and steamed broccoli.
These meals provide a balance of carbohydrates, protein, and micronutrients to fuel your workouts and support cardiovascular health.
Mediterranean and Plant-Based Diets
Research shows that Mediterranean and plant-based diets correlate with higher VO2 max and improved overall health. These diets emphasize whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats like olive oil, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. This combination supports better blood flow and oxygen delivery to muscles, which is essential for endurance.
Moreover, the nutrient-dense nature of these diets ensures your body gets the vitamins and minerals necessary for optimal performance and recovery. Adopting such eating patterns can refine your VO2 max by improving cardiovascular function and reducing inflammation, making them powerful tools for both fitness and long-term health.
Age-Specific Training Considerations
VO2 max naturally declines by about 1% per year after age 30, but this drop can be slowed with smart, targeted training that takes age, gender, and individual health into account. As we get older, it’s important to adjust both the intensity and frequency of workouts, as well as recovery strategies, to match changing physiology.
For adults over 40, longer warm-ups and a gradual increase in intensity help accommodate reduced joint mobility and longer recovery needs. Women, especially post-menopause, may benefit from extra focus on strength training to counteract accelerated muscle and bone loss, while men should pay attention to flexibility and joint health as part of their routine.
Training frequency and style should shift with age and individual needs:
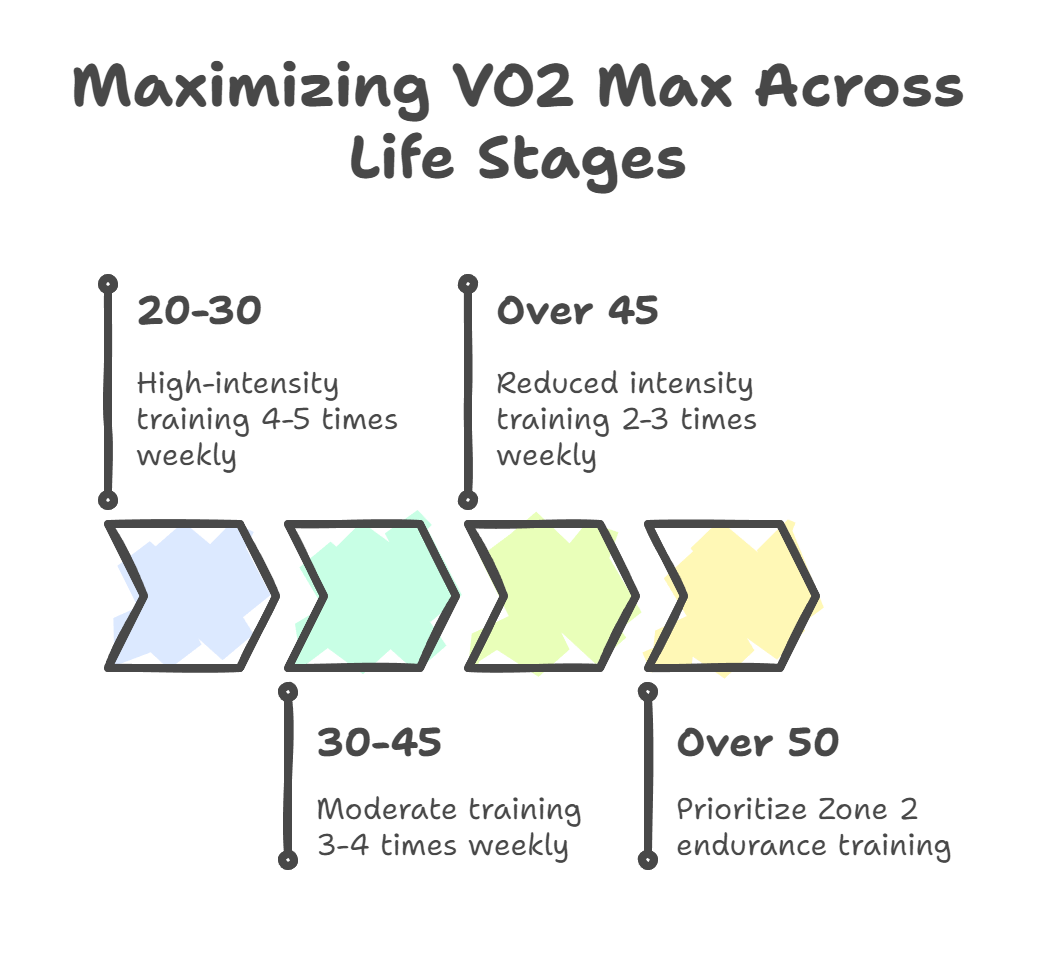
- Younger adults (20-30) can typically handle 4–5 high-intensity sessions per week, thanks to faster recovery and greater resilience.
- Adults 30-45 should scale back to 3–4 sessions weekly, allowing more time for recovery and adaptation.
- Over 45, most people see the best results with 2–3 high-intensity sessions per week, paired with longer recovery periods and a greater emphasis on quality over quantity.
- For those over 50, prioritizing Zone 2 endurance training, like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming at a conversational pace, can deliver similar VO2 max gains as HIIT, but with a lower risk of injury and better adherence.
For both men and women, strength training becomes increasingly important with age. After 40, muscle mass naturally declines (sarcopenia), which can limit oxygen use during exercise. To counter this:
- Aim for 2–3 resistance training sessions per week, focusing on multi-joint movements like squats, lunges, and resistance band exercises.
- Women may need slightly longer recovery periods and should emphasize weight-bearing exercises to maintain bone density.
- Men should include flexibility and mobility work to protect joint health and sustain performance.
No matter your age, gender, or starting point, these principles can help you safely and effectively improve your VO2 max:
- Always begin with a thorough warm-up.
- Progress intensity gradually and listen to your body’s feedback.
- Use progressive overload, that is, slowly increase the challenge to avoid injury.
- If you have chronic conditions or are new to exercise, check with a healthcare professional before starting a new program.
With thoughtful adjustments, everyone can make meaningful improvements in VO2 max and overall cardiovascular fitness at any stage of life.
Beginner vs. Advanced Training Protocols
Beginners should:
- Start with 2-3 training sessions per week at 60-70% maximum heart rate.
- Gradually build an aerobic base before attempting high-intensity protocols to avoid overtraining or injury.
- Focus on general aerobic conditioning and proper form to establish a solid fitness foundation.
Advanced athletes can handle 4-6 training sessions per week with intensities reaching 90-95% maximum heart rate, as their developed cardiovascular systems and training experience allow for greater training loads and faster recovery.
Advanced protocols can include sport-specific training methods and more sophisticated periodization to optimize performance.
Recovery needs scale with training intensity: beginners require 24-48 hours between moderate sessions, while advanced athletes may need 48-72 hours between maximal efforts but can perform active recovery sessions on off days.
Progression timelines also differ significantly, with beginners seeing larger initial improvements, while advanced athletes experience smaller gains due to higher baseline fitness.
The Role of Sleep and Recovery in VO2 Max Improvement
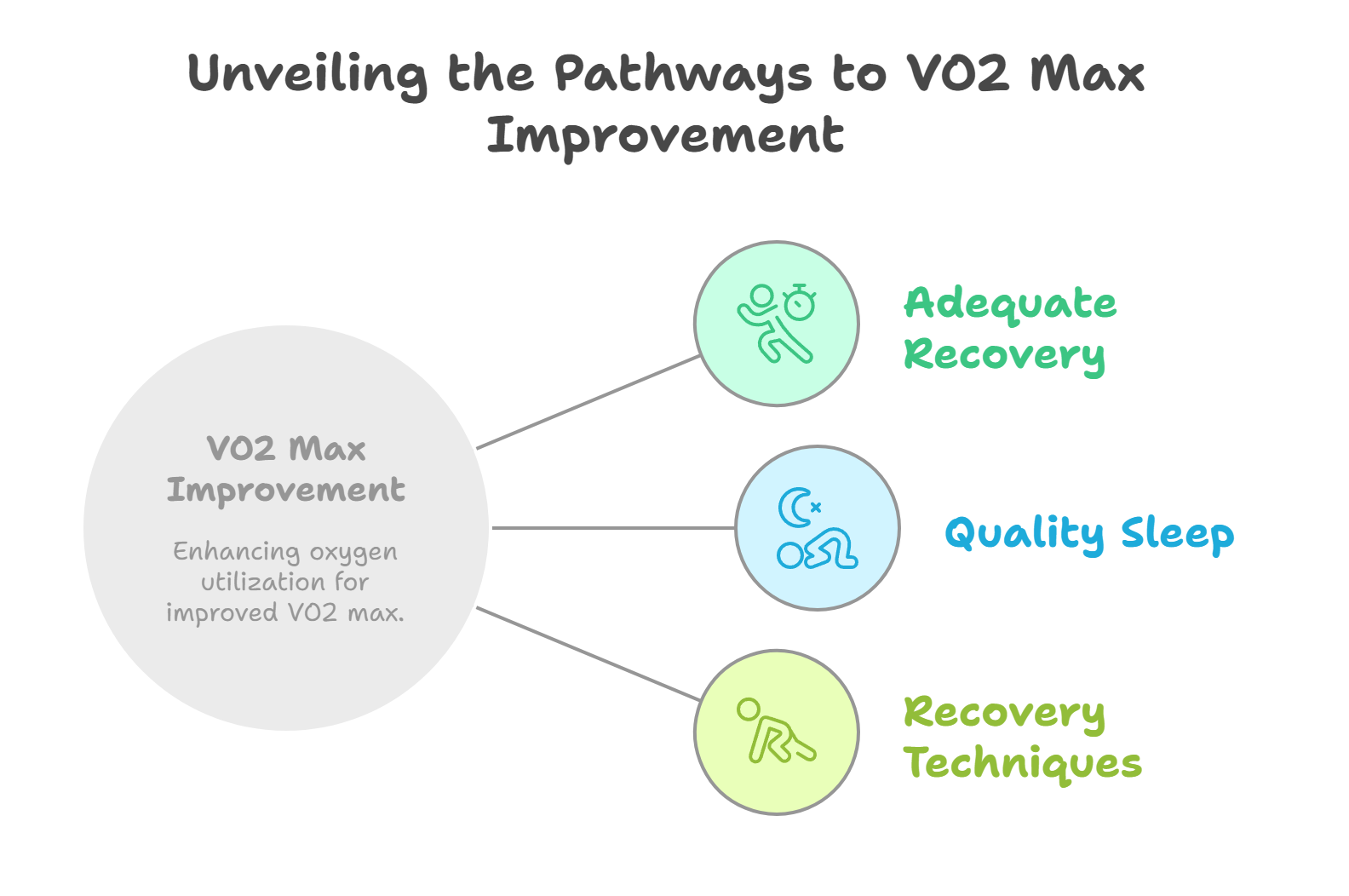
Adequate recovery is important for optimizing training outcomes and improving VO2 max. Inadequate recovery time can lead to stagnation in VO2 max improvement, as the body requires sufficient rest to adapt and make physiological improvements to oxygen utilization capacity.
Monitoring daily activity can help optimize recovery and improve VO2 max performance by ensuring training and rest are balanced effectively.
Importance of Quality Sleep
Quality sleep is equally essential for overall health and contributes to the body’s recovery processes. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support heart function and oxygen uptake capacity.
Endurance training also increases the body’s ability to utilize oxygen efficiently during prolonged exercise, as the body requires oxygen. Ensuring adequate rest supports the recovery and adaptation processes necessary for improving VO2 max for endurance athletes.
Recovery Techniques
Including stretching and active recovery can heighten muscle repair and help maintain training intensity. Active recovery promotes muscle repair and helps sustain high training intensity, making it an essential component of any effective training program.
Techniques such as:
- Foam rolling,
- Low-intensity cycling, and
- Yoga,
can aid in muscle recovery and flexibility, reducing the risk of injury and promoting overall fitness.
Common Mistakes and What to Avoid
Overtraining is the most frequent mistake when attempting to improve VO2 max, with many athletes believing more intense training always equals better results. Inadequate recovery time can lead to stagnation in VO2 max improvement, as the body requires 24-72 hours between high-intensity sessions to adapt and make physiological improvements to oxygen utilization capacity.
Focusing solely on one training modality limits VO2 max potential, as exclusive reliance on either only HIIT or only steady-state training fails to develop the full spectrum of cardiovascular adaptations.
Sacrificing sleep quality undermines all training efforts, as inadequate sleep impairs recovery, reduces training adaptation, and limits the body’s ability to improve oxygen utilization capacity.
Ensuring balanced training, proper nutrition, and adequate rest are key, but not everyone avoids these common pitfalls.
Measuring and Tracking VO2 Max
Understanding your VO2 max is a powerful tool for designing effective workouts and tracking your fitness progress. VO2 max is expressed in milliliters of oxygen consumed per kilogram of body weight per minute (mL/kg/min), reflecting how efficiently your body uses oxygen during exercise.
Laboratory Testing
The most accurate way to measure VO2 max is through a laboratory test, typically performed on a treadmill or stationary bike. During this test, exercise intensity gradually increases until you reach your maximum effort. The most accurate measurement of VO2 max takes place in an exercise medicine lab, where specialized equipment and protocols ensure precise results.
You wear a mask that measures the oxygen you inhale and the carbon dioxide you exhale, providing precise data on your aerobic capacity. This method, known as mask analysis during a maximal treadmill test, remains the gold standard for VO2 max measurement.
Wearable Technology
For those without access to lab testing, many smartwatches and fitness trackers offer VO2 max estimates using heart rate and GPS data. Brands like Garmin, Apple Watch, and Polar use algorithms to calculate VO2 max during activities like running and cycling.
While these estimates may not be as precise as lab tests, they allow you to track trends over time and adjust your training accordingly.
Wearable Comparison Snapshot:
| Device | Activity Types Used | Accuracy Level | Additional Features |
| Garmin | Running, Cycling | Moderate to High | Training load, recovery advisor |
| Apple Watch | Running, Walking, Cycling | Moderate | Hear rate variability, ECG |
| Polar | Running, Cycling, Swimming | Moderate to High | Detailed training insights |
Accuracy depends on sensor quality and user consistency.
Sub-Maximal Tests
If you can’t access lab testing or wearables, sub-maximal tests provide a practical way to estimate VO2 max. One well-validated method is the 1-mile walk test, which uses your walk time, heart rate, age, weight, and gender to predict VO2 max with reasonable accuracy.
Other common sub-maximal tests include the Cooper 12-minute run/walk test and the Astrand-Rhyming cycle ergometer test. Among these, the Cooper test has shown the strongest correlation with lab-measured VO2 max (correlation coefficient ~0.92), making it a reliable option for runners and walkers alike.
VO2 Max Calculator: 1-Mile Walk Test
Try estimating your VO2 max using the 1-mile walk test formula below. Enter your details to see your estimated aerobic capacity:
| Input Field | Description |
| Weight (kg) | Your body weight |
| Age | Your age |
| Gender | Male / Female |
| Walk Time (minutes:seconds) | Time taken to walk 1 mile |
| Heart Rate (bpm) | Heart rate immediately after walk |
Formula used (simplified example):
VO2 max = 132.853 – (0.0769 × Weight) – (0.3877 × Age) + (6.315 × Gender) – (3.2649 × Walk Time in minutes) – (0.1565 × Heart Rate)
(Gender: Male = 1, Female = 0)
Tracking your VO2 max regularly, no matter the method, helps you monitor improvements and tailor workouts to your fitness level.
Benefits of Improving VO2 Max
A higher VO2 max is a powerful marker of overall health and fitness. It reflects how efficiently your heart, lungs, and muscles work together to deliver and use oxygen during exercise. Improving your VO2 max can lower the risk of developing cardiovascular disease by reducing heart strain and supporting better heart health. Beyond athletic performance, improving your VO2 max offers significant benefits for your long-term health and daily life.
Cardiovascular Health
Higher VO2 max levels are linked to better heart function and efficiency. This means your heart pumps blood more effectively, reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and certain cancers. Exercise that raises VO2 max also improves blood pressure, lipid profiles, and lung capacity, supporting overall respiratory and cardiovascular health.
That said, improving your VO2 max isn’t just about sports, it’s about improving the quality of your life.
Athletic Performance
For athletes, a higher VO2 max allows maintaining faster paces and sustaining effort longer during endurance activities. It’s a key factor in physical fitness, enabling better performance and quicker recovery.
By focusing on boosting your VO2 max, you’re not only improving your athletic potential but also building a foundation for a healthier lifestyle.
VO2 Max Norms by Age and Gender
Compare your VO2 max to these norms to gauge your fitness level:
| Age Group | Male (mL/kg/min) | Female (mL/kg/min) |
| 20-29 | 42-46 | 35-38 |
| 30-39 | 39-43 | 33-36 |
| 40-49 | 36-41 | 30-34 |
| 50-59 | 33-37 | 27-31 |
| 60-69 | 30-35 | 24-28 |
| 70+ | 26-31 | 20-25 |
Values represent average ranges for non-athletes.
Whether your goal is to improve endurance, boost heart health, or simply feel more energetic in daily life, raising your VO2 max is a proven path to better fitness and well-being.
Sample Training Plans for VO2 Max Improvement
Improving your VO2 max requires a structured plan that balances high-intensity intervals with steady-state and tempo training. Therefore, adding variety not only maximizes cardiovascular gains but also helps prevent plateaus and reduces injury risk.
Below is a 4-week sample training plan designed to progressively boost your VO2 max. It combines HIIT sessions, tempo runs, endurance workouts, and body-weight circuit training, with built-in rest and recovery days to optimize adaptation.
| Day | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 |
| Monday | HIIT: 4×4 min intervals at 90-95% max HR, 4 min rest | HIIT: 5×4 min intervals at 90-95% max HR, 4 min rest | HIIT: 6×4 min intervals at 90-95% max HR, 3 min rest | HIIT: 4×5 min intervals at 90-95% max HR, 3 min rest |
| Tuesday | Zone 2 Endurance: 45 min easy run or cycling | Zone 2 Endurance: 50 min steady pace | Zone 2 Endurance: 60 min steady pace | Zone 2 Endurance: 60 min steady pace |
| Wednesday | Body-weight circuit training (push-ups, squats, lunges, burpees; 3 rounds) | Body-weight circuit training (4 rounds) | Body-weight circuit training (4 rounds) | Body-weight circuit training (5 rounds) |
| Thursday | Tempo run: 20 min at lactate threshold pace | Tempo run: 25 min at lactate threshold pace | Tempo run: 30 min at lactate threshold pace | Tempo intervals: 3×10 min at threshold pace with 2 min jog recovery |
| Friday | Rest or active recovery (light walking, stretching) | Rest or active recovery | Rest or active recovery | Rest or active recovery |
| Saturday | Long endurance: 60-75 min Zone 2 run or bike | Long endurance: 75-90 min Zone 2 run or bike | Long endurance: 75-90 min Zone 2 run or bike | Long endurance: 90 min Zone 2 run or bike |
| Sunday | Rest or light cross-training (swimming, yoga) | Rest or light cross-training | Rest or light cross-training | Rest or light cross-training |
Key Points to Maximize VO2 Max Gains
- HIIT sessions push your heart rate to 90-95% of maximum, stimulating cardiovascular adaptations crucial for improving VO2 max. Start with fewer intervals and gradually increase volume and intensity.
- Tempo runs target your lactate threshold, helping you sustain higher intensities for longer.
- Zone 2 endurance workouts build your aerobic base, improving fat metabolism and mitochondrial function.
- Body-weight circuit training strengthens muscles and supports cardiovascular fitness simultaneously, aiding overall aerobic capacity.
- Rest days and active recovery are essential to allow your body to repair and adapt.
Mixing up your workouts, alternating running, cycling, swimming, or rowing, can prevent boredom and provide diverse cardiovascular stimuli, further enhancing your VO2 max.
Summary
Unlocking your full cardiovascular potential starts with understanding and improving your VO2 max. By integrating high-intensity intervals, Zone 2 endurance, and threshold training into your routine, you set the stage for lasting fitness gains and enhanced overall health.
Consistency and a well-rounded approach are your best allies. Supplement these workouts with targeted nutrition and recovery strategies to maximize results. At RX Fits, we specialize in crafting personalized plans that help you boost your VO2 max safely and effectively.
Contact RxFit todayBook A Free Assessment Now
Frequently Asked Questions
What is VO2 max and why is it important?
VO2 max is an important measure of your body’s maximum oxygen usage during exercise, reflecting your cardiovascular fitness and overall health. Improving your VO2 max can improve your endurance and athletic performance.
How can I improve my VO2 max quickly?
To quickly improve your VO2 max, incorporate High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) into your routine, as it alternates intense efforts with recovery periods for maximum benefit. This method is proven to yield effective results in a short timeframe.
What role does nutrition play in improving VO2 max?
Nutrition plays a fundamental role in improving VO2 max by providing the necessary fuel for intense training and promoting recovery. A focus on higher carbohydrate intake and adopting a Mediterranean or plant-based diet can significantly increase your performance and overall results.
How does age affect VO2 max?
Age affects VO2 max by causing a natural decline, but engaging in targeted training can mitigate this decrease and enhance cardiovascular fitness regardless of age.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when trying to improve VO2 max?
To effectively improve your VO2 max, avoid common mistakes such as overtraining, neglecting recovery, and solely relying on one type of exercise. Instead, prioritize balanced training, proper nutrition, and quality sleep.
![How to Improve VO2 Max Quickly And Effectively [Definitive Guide] RxFit logo featuring bold lettering and a dynamic design, representing a fitness service provider focused on health and wellness.](https://rxfit.co/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/cropped-Untitled-design-1-1.jpg)